24 Animal Cell Nucleus Structure
They have well-organized cell organelles that perform different functions such as plasma membrane centriole peroxisome lysosome ribosomes mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum cytoplasm nucleus nucleolus nuclear envelope and golgi apparatus. It stores the cells hereditary material or DNA and it coordinates the cells.
/human-cells--illustration-623682423-5c48d355c9e77c00011f4744.jpg)
The Nucleus Definition Structure And Function
This animation by Nucleus shows you the function of plant and animal cells for middle school and high school biology including organelles like the nucleus.
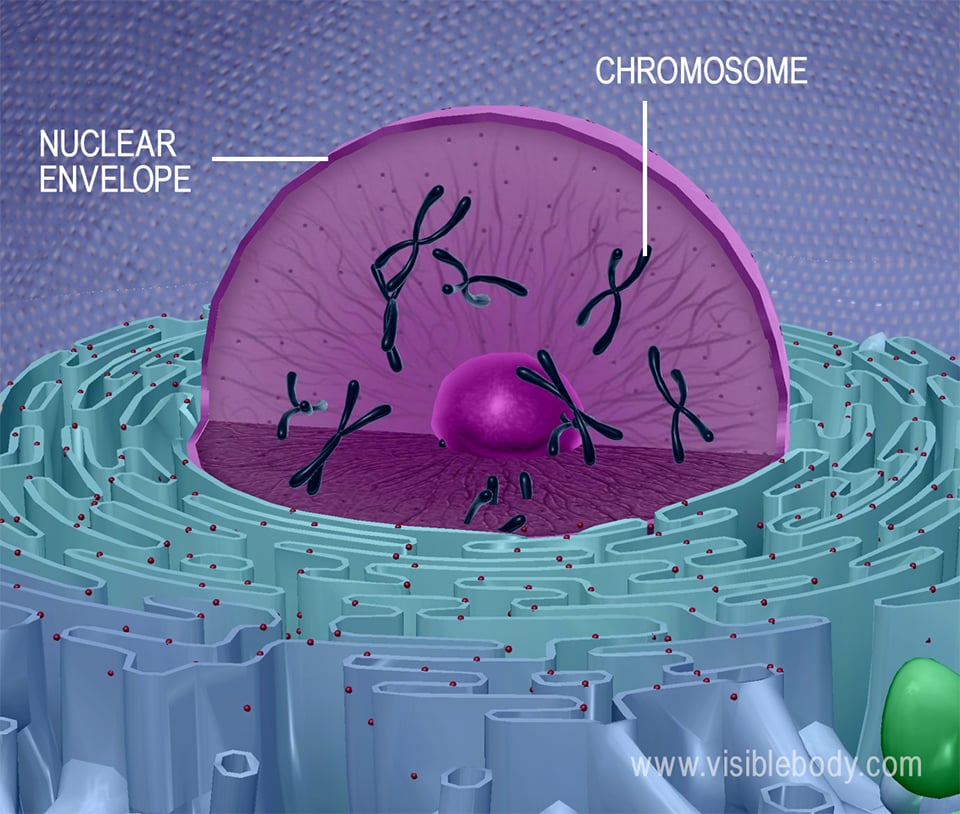
Animal cell nucleus structure. Unlike prokaryotic cells DNA in animal cells is housed within the nucleus. An animal cell is defined as the basic structural and functional unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. Nucleus - The nucleus is a highly specialized organelle that serves as the information processing and administrative center of the cell.
A generalised animal cell and its components Mitochondria singular. Mitochondria - Mitochondria are oblong shaped organelles that are found in the cytoplasm of every eukaryotic cell. Function of Cell Nucleus.
Animal Cell Nucleus. 3d Cell Model Project Cells Project Animal Cell Cell Model Project Cell structure overview the major parts of the cell are the nucleus the control center. The nucleus is completely bound by membranes.
It is the main control center for the cell and acts kind of like the cells brain. The cell nucleus is a large organelle in eukaryotic organisms which protects the majority of. A major structure in the nucleus is Nucleolus and animal cell nucleus function is to help to synthesize protein and produce ribosomes.
Jul 7 2013 teaching the cell can be fun and engaging for students. Contained within the nucleus is a dense membrane-less structure composed of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus. Legend opens a modal possible mastery.
Animal cell nucleus is an organelle attached to membrane enclosed by dual membrane. The nucleolus helps to synthesize ribosomes by transcribing and assembling ribosomal RNA subunits. Cell Nucleus Cell Nucleus Definition.
The membrane distinguishes the cytoplasm from the contents of. It is engirdled by a structure referred to as the nuclear envelope. Just like an envelope surrounding a letter the nuclear envelope contains all.
The nucleus is perhaps the most important structure inside animal and plant cells. It stores the cells hereditary material or DNA and it coordinates the cells activities which include intermediary metabolism growth protein synthesis and reproduction cell division. Cells prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Biology high school animal cell diagram. The animal cells have an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope. They have a distinct nucleus with all cellular organelles enclosed in a membrane and thus called a eukaryotic cell.
This organelle has two major functions. Animal cells are eukaryotic cells or cells with a membrane-bound nucleus. Structure Of Nucleus Typically it is the most evident organelle in the cell.
A cell nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane known as the nuclear envelope. The nucleolus contains nucleolar organizers the parts of chromosomes carrying the genes for ribosome synthesis. The nucleus is a highly specialized organelle that serves as the information and administrative center of the cell.
This means they have a nucleus and other structures which are surrounded by membranes. The nucleus has an outer barrier called the nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane surrounding it. In addition to having a nucleus animal cells also contain other membrane-bound organelles or tiny cellular structures that carry out specific functions necessary for normal cellular operation.
In the animal cell they are the main power generators converting oxygen and nutrients into energy. These cells are eukaryotic. This organelle has two major functions.
Only eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. In fact the definition of a eukaryotic cell is that it contains a nucleus while. Structure and Characteristics of an Animal Cell.
Along with that it possesses locomotory structures. The nuclear pores allow communication between the nucleus and the neighboring cell cytoplasm.
